Note
Go to the end to download the full example code.
Direction definition example#
This example shows how to define directions from lookup tables. They can be either reference directions for oriented selection sets or draping angles for modeling plies. The example only shows the PyACP part of the setup. For a complete composite analysis, see PyMAPDL workflow.
Import modules#
Import the standard library and third-party dependencies.
import pathlib
import tempfile
import numpy as np
Import the PyACP dependencies.
from ansys.acp.core import (
ACPWorkflow,
DimensionType,
DrapingType,
LookUpTableColumnValueType,
PlyType,
RosetteSelectionMethod,
get_directions_plotter,
launch_acp,
)
from ansys.acp.core.extras import ExampleKeys, get_example_file
Start ACP and load the model#
Get the example file from the server.
tempdir = tempfile.TemporaryDirectory()
WORKING_DIR = pathlib.Path(tempdir.name)
input_file = get_example_file(ExampleKeys.BASIC_FLAT_PLATE_DAT, WORKING_DIR)
Launch the PyACP server and connect to it.
acp = launch_acp()
Define the input file and instantiate an ACPWorkflow instance.
The ACPWorkflow class provides convenience methods that simplify the handling.
It automatically creates a model based on the input file.
This example’s input file contains a flat plate with a single ply.
workflow = ACPWorkflow.from_cdb_or_dat_file(
acp=acp,
cdb_or_dat_file_path=input_file,
local_working_directory=WORKING_DIR,
)
model = workflow.model
print(workflow.working_directory.path)
print(model.unit_system)
/tmp/tmpul4irke5
mks
Setup materials and oriented selection set#
#
Create a material and fabric.
ud_material = model.create_material(
name="UD",
ply_type=PlyType.REGULAR,
)
fabric = model.create_fabric(name="UD", material=ud_material, thickness=0.1)
Create a parallel rosette.
rosette = model.create_rosette()
Create an oriented selection set (OSS) and assign the rosette.
oss = model.create_oriented_selection_set(
name="oss",
orientation_direction=(0.0, 1.0, 0),
element_sets=[model.element_sets["All_Elements"]],
rosettes=[rosette],
)
Plot the orientation and reference direction of the OSS. The reference direction is defined by the rosette.
model.update()
plotter = get_directions_plotter(
model=model, components=[oss.elemental_data.orientation, oss.elemental_data.reference_direction]
)
plotter.show()
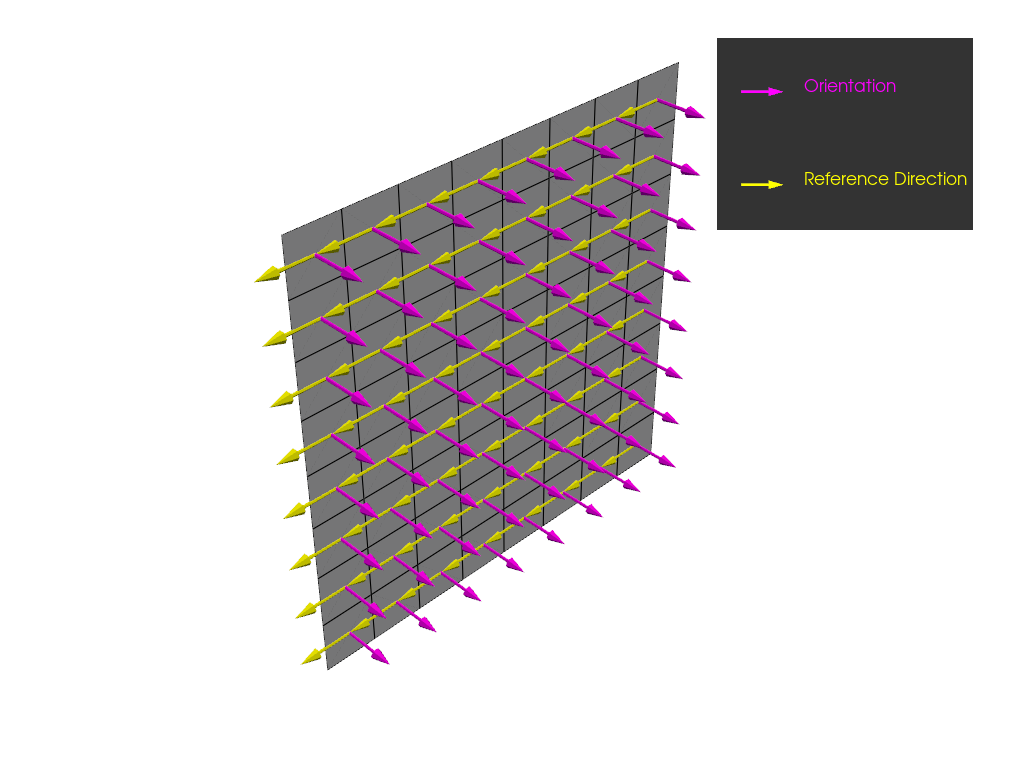
Define reference direction from lookup table#
Create a 3D lookup table to store the direction and angle corrections.
lookup_table = model.create_lookup_table_3d()
Create a grid of points on the plate where the lookup table values are stored.
plate_side_length = 0.01
num_points = 10
x_coordinates = np.linspace(0, plate_side_length, num_points)
z_coordinates = np.linspace(0, plate_side_length, num_points)
xx, zz = np.meshgrid(x_coordinates, z_coordinates)
points = np.stack(
[
xx.ravel(),
np.zeros(xx.ravel().shape),
zz.ravel(),
],
axis=1,
)
Compute the directions tangential to circles around the point (0,0,0).
Create the lookup table and add the direction data.
lookup_table.columns["Location"].data = points
direction_column = lookup_table.create_column(
data=directions,
dimension_type=DimensionType.DIMENSIONLESS,
value_type=LookUpTableColumnValueType.DIRECTION,
)
Assign the lookup table to the OSS.
oss.rosette_selection_method = RosetteSelectionMethod.DIRECTIONS_FROM_TABULAR_VALUES
oss.reference_direction_field = direction_column
Plot the orientation and the reference direction of the OSS.
model.update()
plotter = get_directions_plotter(
model=model, components=[oss.elemental_data.orientation, oss.elemental_data.reference_direction]
)
plotter.show()
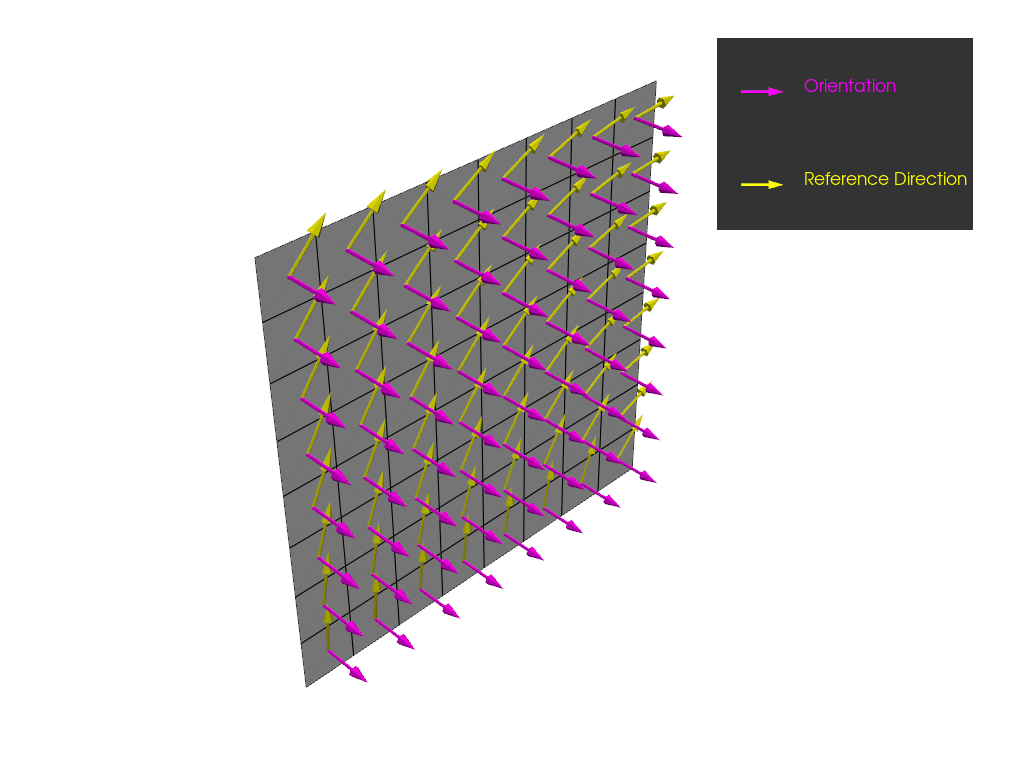
Reset the OSS so that it may use the rosette again for the reference direction.
oss.rosette_selection_method = RosetteSelectionMethod.MINIMUM_ANGLE
Define draping angles from lookup table#
%% Compute a correction angle to define circular fiber paths.
correction_angle = np.arctan2(xx.ravel(), zz.ravel()) * 180 / np.pi
angle_column_1 = lookup_table.create_column(
data=correction_angle,
dimension_type=DimensionType.DIMENSIONLESS,
value_type=LookUpTableColumnValueType.SCALAR,
)
Compute the transverse correction angle, assuming a constant shear angle of -30°.
shear_angle = -30
transverse_correction_angle = correction_angle + shear_angle
angle_column_2 = lookup_table.create_column(
data=transverse_correction_angle,
dimension_type=DimensionType.DIMENSIONLESS,
value_type=LookUpTableColumnValueType.SCALAR,
)
Create a modeling ply with the angle corrections.
modeling_group = model.create_modeling_group(name="modeling_group")
modeling_ply = modeling_group.create_modeling_ply(
name="ply",
ply_angle=0,
ply_material=fabric,
oriented_selection_sets=[oss],
draping_type=DrapingType.TABULAR_VALUES,
draping_angle_1_field=angle_column_1,
draping_angle_2_field=angle_column_2,
)
Plot the directions of the modeling ply. First, plot the directions without correction angles.
model.update()
plotter = get_directions_plotter(
model=model,
components=[
modeling_ply.elemental_data.fiber_direction,
modeling_ply.elemental_data.transverse_direction,
],
)
plotter.show()
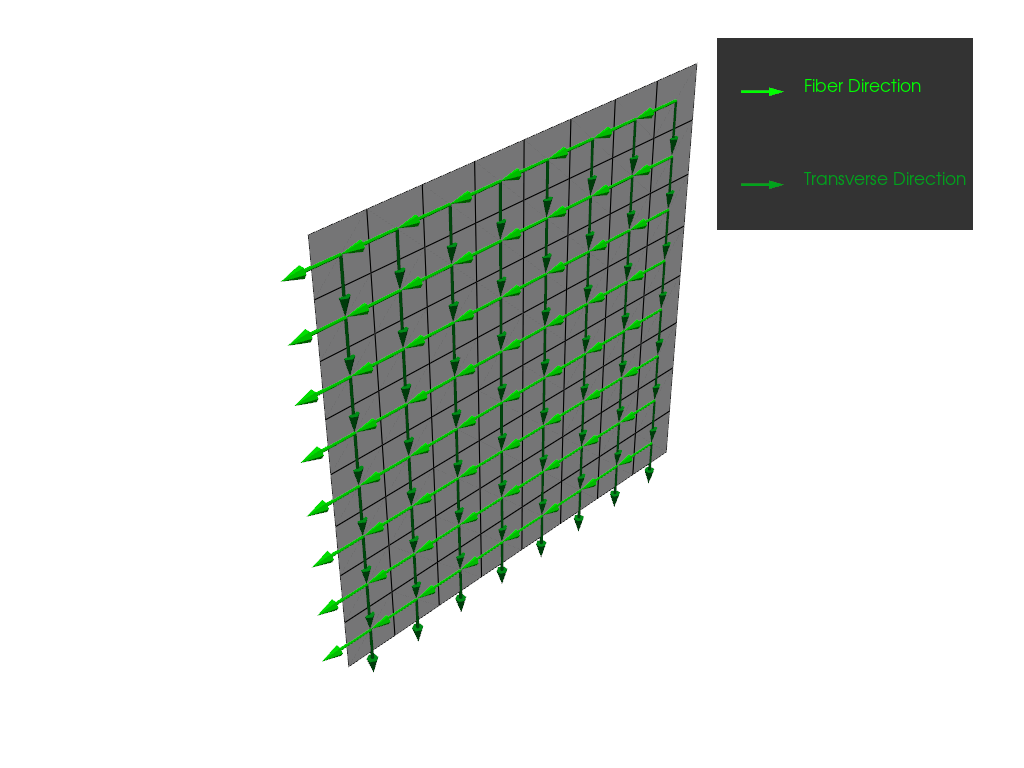
Next, plot the draped directions, including the correction angles, from the lookup table.
plotter = get_directions_plotter(
model=model,
components=[
modeling_ply.elemental_data.draped_fiber_direction,
modeling_ply.elemental_data.draped_transverse_direction,
],
)
plotter.show()
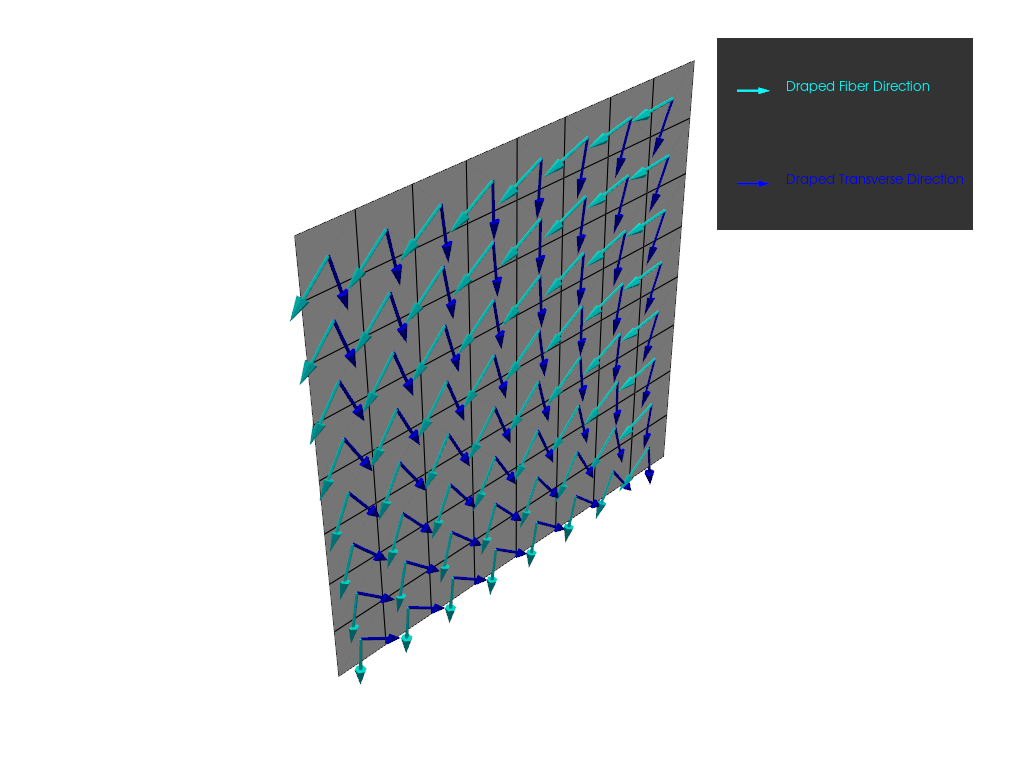
Total running time of the script: (0 minutes 5.324 seconds)

