Note
Go to the end to download the full example code.
Advanced rules example#
This example shows how to use advanced rules, including the geometrical, cut-off, and variable offset rules. It also demonstrates how rules can be templated and reused with different parameters. For more basic rules, see Basic selection rules example.
This example only shows the PyACP part of the setup. For a complete composite analysis, see Basic PyACP workflow example.
Import modules#
Import the standard library and third-party dependencies.
import pathlib
import tempfile
import numpy as np
import pyvista
Import the PyACP dependencies.
from ansys.acp.core import (
ACPWorkflow,
BooleanOperationType,
DimensionType,
EdgeSetType,
LinkedSelectionRule,
example_helpers,
launch_acp,
)
from ansys.acp.core.example_helpers import ExampleKeys, get_example_file
Start ACP and load the model#
Get the example file from the server.
tempdir = tempfile.TemporaryDirectory()
WORKING_DIR = pathlib.Path(tempdir.name)
input_file = get_example_file(ExampleKeys.MINIMAL_FLAT_PLATE, WORKING_DIR)
Launch the PyACP server and connect to it.
acp = launch_acp()
Define the input file and instantiate an ACPWorkflow instance.
The ACPWorkflow class provides convenience methods that simplify file handling.
It automatically creates a model based on the input file.
This example’s input file contains a flat plate with a single ply.
workflow = ACPWorkflow.from_acph5_file(
acp=acp,
acph5_file_path=input_file,
local_working_directory=WORKING_DIR,
)
model = workflow.model
print(workflow.working_directory.path)
print(model.unit_system)
/tmp/tmp_cevrsj3
mks
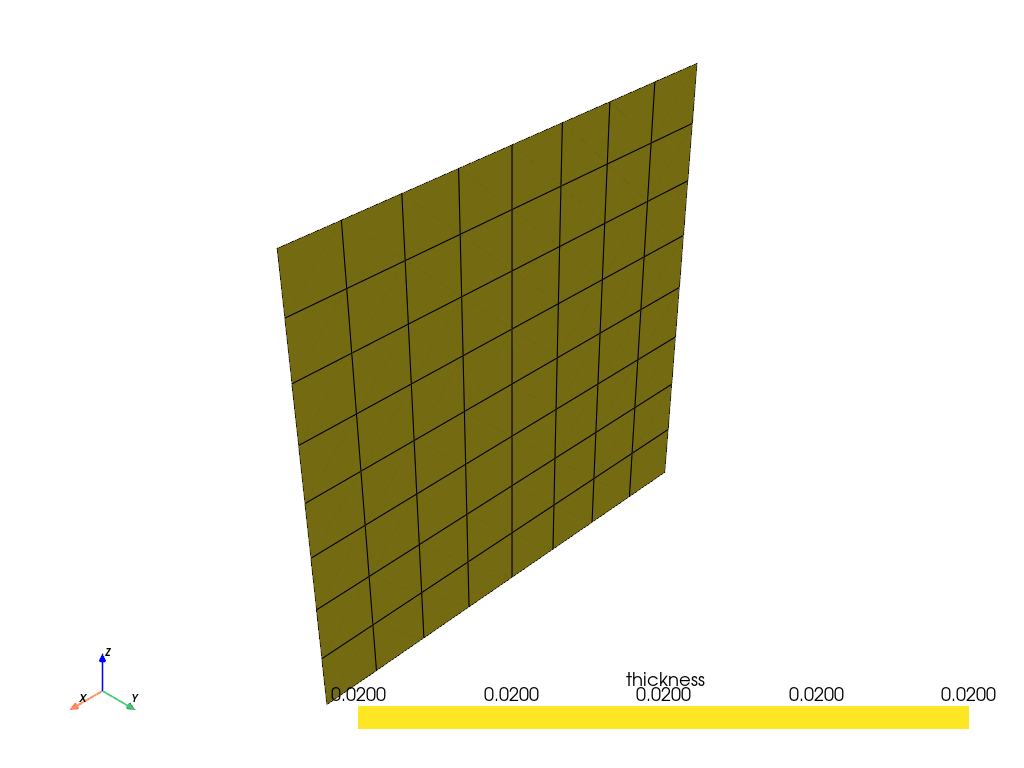
Add more layers to the modeling ply so that it is easier to see the effects of the selection rules. Plot the thickness of all the plies without any rules.
modeling_ply = model.modeling_groups["modeling_group"].modeling_plies["ply"]
modeling_ply.number_of_layers = 10
model.update()
assert model.elemental_data.thickness is not None
model.elemental_data.thickness.get_pyvista_mesh(mesh=model.mesh).plot(show_edges=True)
Parametrized Parallel Rule#
Rules can be parametrized. This is useful when a rule is used multiple times but with different
parameters. The LinkedSelectionRule class shows what parameters are available for each rule.
This code modifies the extent of the parallel rule.
Create a parallel rule.
parallel_rule = model.create_parallel_selection_rule(
name="parallel_rule",
origin=(0, 0, 0),
direction=(1, 0, 0),
lower_limit=0.005,
upper_limit=1,
)
Assign it the modeling ply.
linked_parallel_rule = LinkedSelectionRule(parallel_rule)
modeling_ply.selection_rules = [linked_parallel_rule]
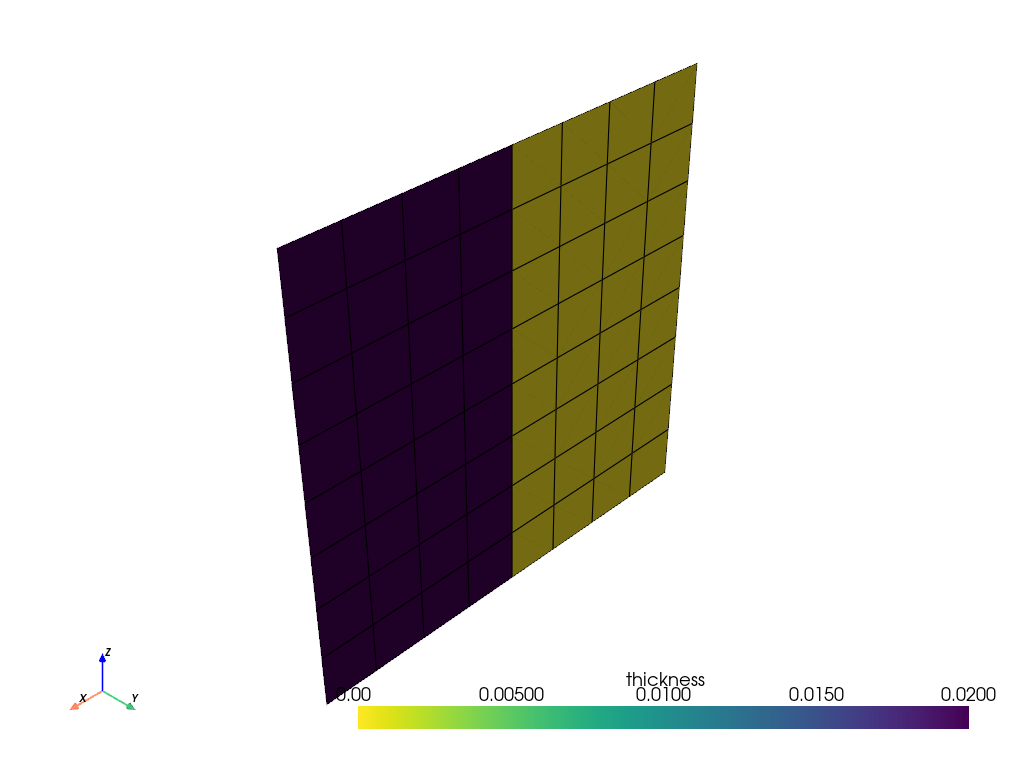
Plot the thickness of the ply before the parametrization.
model.update()
assert model.elemental_data.thickness is not None
model.elemental_data.thickness.get_pyvista_mesh(mesh=model.mesh).plot(show_edges=True)
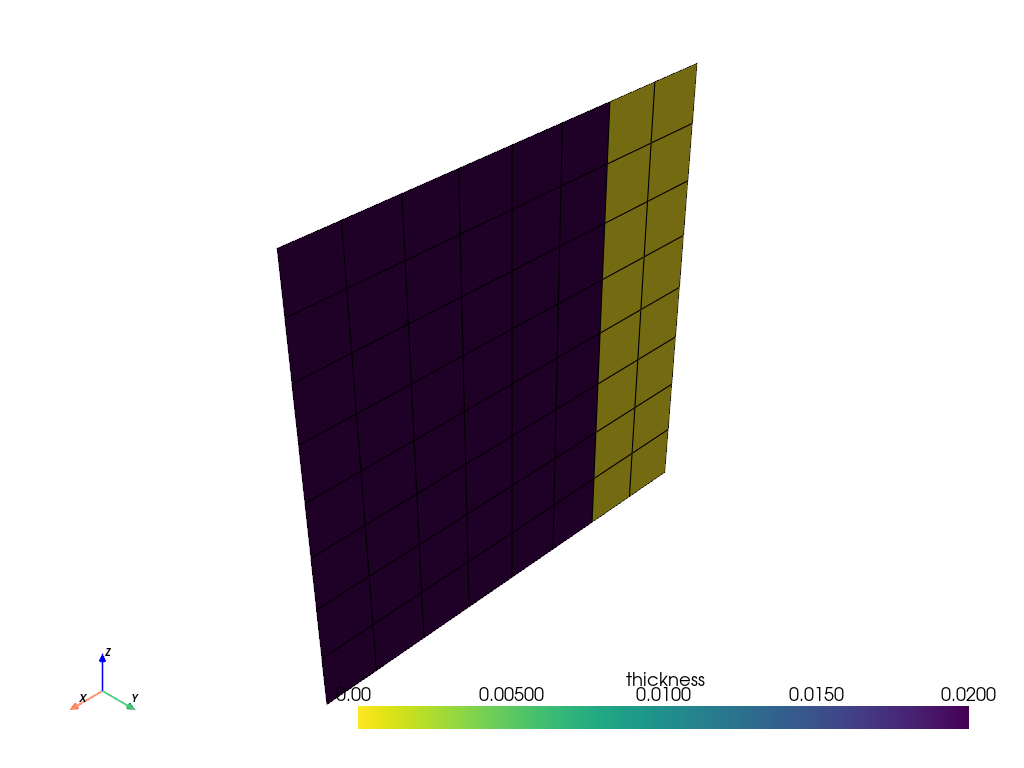
Modify the parallel rule by changing the parameters of the linked rule. Parameters defined on the linked rule override the parameters of the original rule.
linked_parallel_rule.template_rule = True
linked_parallel_rule.parameter_1 = 0.002
linked_parallel_rule.parameter_2 = 0.1
Plot the thickness of the ply with the modified rule.
model.update()
assert model.elemental_data.thickness is not None
model.elemental_data.thickness.get_pyvista_mesh(mesh=model.mesh).plot(show_edges=True)
Create a geometrical selection rule#
Add a CAD geometry to the model.
triangle_path = example_helpers.get_example_file(
example_helpers.ExampleKeys.RULE_GEOMETRY_TRIANGLE, WORKING_DIR
)
triangle = workflow.add_cad_geometry_from_local_file(triangle_path)
# Note: It is important to update the model here, because the root_shapes of the
# cad_geometry are not available until the model is updated.
model.update()
Create a virtual geometry from the CAD geometry.
triangle_virtual_geometry = model.create_virtual_geometry(
name="triangle_virtual_geometry", cad_components=triangle.root_shapes.values()
)
Create the geometrical selection rule.
geometrical_selection_rule = model.create_geometrical_selection_rule(
name="geometrical_rule",
geometry=triangle_virtual_geometry,
)
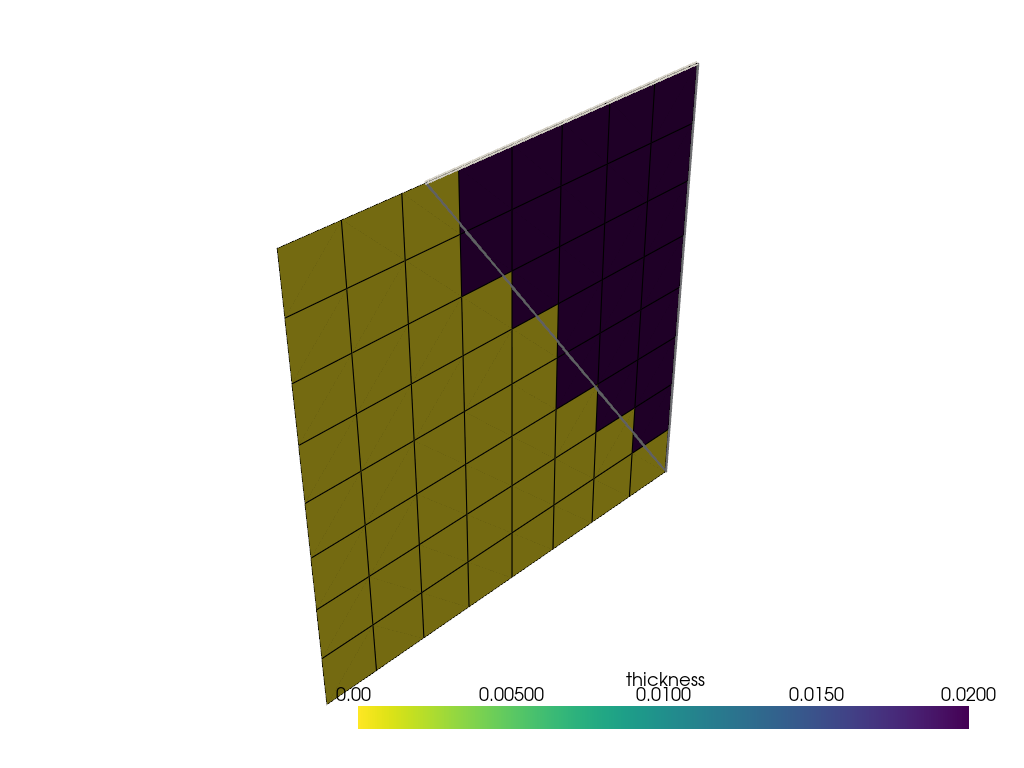
Assign the geometrical selection rule to the ply. Plot the ply extent with the outline of the geometry.
modeling_ply.selection_rules = [LinkedSelectionRule(geometrical_selection_rule)]
model.update()
assert model.elemental_data.thickness is not None
plotter = pyvista.Plotter()
plotter.add_mesh(
triangle.visualization_mesh.to_pyvista(), style="wireframe", line_width=4, color="white"
)
plotter.add_mesh(model.elemental_data.thickness.get_pyvista_mesh(mesh=model.mesh), show_edges=True)
plotter.show()
Create a cutoff selection rule#
Add the cutoff CAD geometry to the model.
cutoff_plane_path = example_helpers.get_example_file(
example_helpers.ExampleKeys.CUT_OFF_GEOMETRY, WORKING_DIR
)
cut_off_plane = workflow.add_cad_geometry_from_local_file(cutoff_plane_path)
# Note: It is important to update the model here, because the root_shapes of the
# cad_geometry are not available until the model is updated.
model.update()
Create a virtual geometry from the CAD geometry.
cutoff_virtual_geometry = model.create_virtual_geometry(
name="cutoff_virtual_geometry", cad_components=cut_off_plane.root_shapes.values()
)
Create the cutoff selection rule.
cutoff_selection_rule = model.create_cutoff_selection_rule(
name="cutoff_rule",
cutoff_geometry=cutoff_virtual_geometry,
)
Assign the cutoff selection rule to the ply. Plot the ply extent with the outline of the geometry.
modeling_ply.selection_rules = [LinkedSelectionRule(cutoff_selection_rule)]
model.update()
assert model.elemental_data.thickness is not None
plotter = pyvista.Plotter()
plotter.add_mesh(cut_off_plane.visualization_mesh.to_pyvista(), color="white")
plotter.add_mesh(model.elemental_data.thickness.get_pyvista_mesh(mesh=model.mesh))
plotter.camera_position = [(-0.05, 0.01, 0), (0.005, 0.005, 0.005), (0, 1, 0)]
plotter.show()
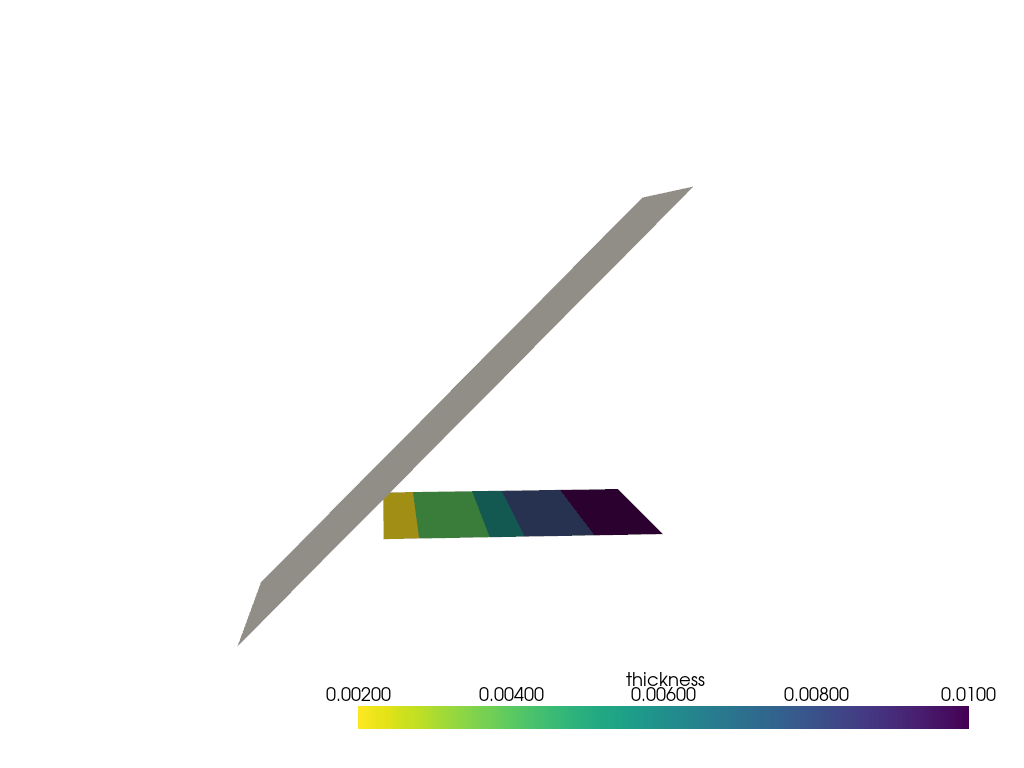
Create a variable offset selection rule#
Create the lookup table.
lookup_table = model.create_lookup_table_1d(
name="lookup_table",
origin=(0, 0, 0),
direction=(0, 0, 1),
)
Add the location data. The “Location” column of the lookup table is always created by default.
lookup_table.columns["Location"].data = np.array([0, 0.005, 0.01])
Create the offset column that defines the offsets from the edge.
offsets_column = lookup_table.create_column(
name="offset",
dimension_type=DimensionType.LENGTH,
data=np.array([0.00, 0.004, 0]),
)
Create the edge set from the “All_Elements” element set. Because you assigned 30 degrees to the limit angle, only one edge at x=0 is selected.
edge_set = model.create_edge_set(
name="edge_set",
edge_set_type=EdgeSetType.BY_REFERENCE,
limit_angle=30,
element_set=model.element_sets["All_Elements"],
origin=(0, 0, 0),
)
Create the variable offset rule and assign it to the ply.
variable_offset_rule = model.create_variable_offset_selection_rule(
name="variable_offset_rule", edge_set=edge_set, offsets=offsets_column, distance_along_edge=True
)
modeling_ply.selection_rules = [LinkedSelectionRule(variable_offset_rule)]
Plot the ply extent.
model.update()
assert model.elemental_data.thickness is not None
model.elemental_data.thickness.get_pyvista_mesh(mesh=model.mesh).plot(show_edges=True)
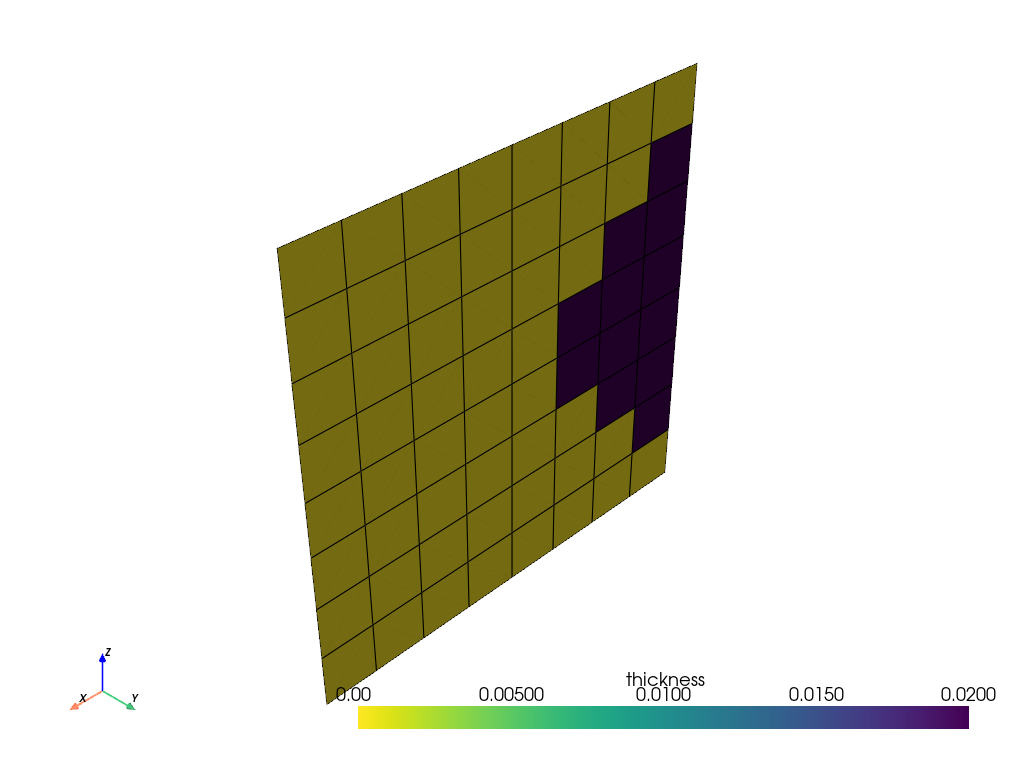
Create a boolean selection rule#
Creating a Boolean selection rule and assigning it to a ply has the same effect as linking the individual rules directly to the ply. Boolean rules are still useful because they can help organize rules and make more complex ones.
Create a cylindrical selection rule to combine with the parallel rule.
cylindrical_rule_boolean = model.create_cylindrical_selection_rule(
name="cylindrical_rule",
origin=(0.005, 0, 0.005),
direction=(0, 1, 0),
radius=0.002,
)
parallel_rule_boolean = model.create_parallel_selection_rule(
name="parallel_rule",
origin=(0, 0, 0),
direction=(1, 0, 0),
lower_limit=0.005,
upper_limit=1,
)
linked_cylindrical_rule_boolean = LinkedSelectionRule(cylindrical_rule_boolean)
linked_parallel_rule_boolean = LinkedSelectionRule(parallel_rule_boolean)
boolean_selection_rule = model.create_boolean_selection_rule(
name="boolean_rule",
selection_rules=[linked_parallel_rule_boolean, linked_cylindrical_rule_boolean],
)
modeling_ply.selection_rules = [LinkedSelectionRule(boolean_selection_rule)]
Plot the ply extent.
model.update()
assert model.elemental_data.thickness is not None
model.elemental_data.thickness.get_pyvista_mesh(mesh=model.mesh).plot(show_edges=True)
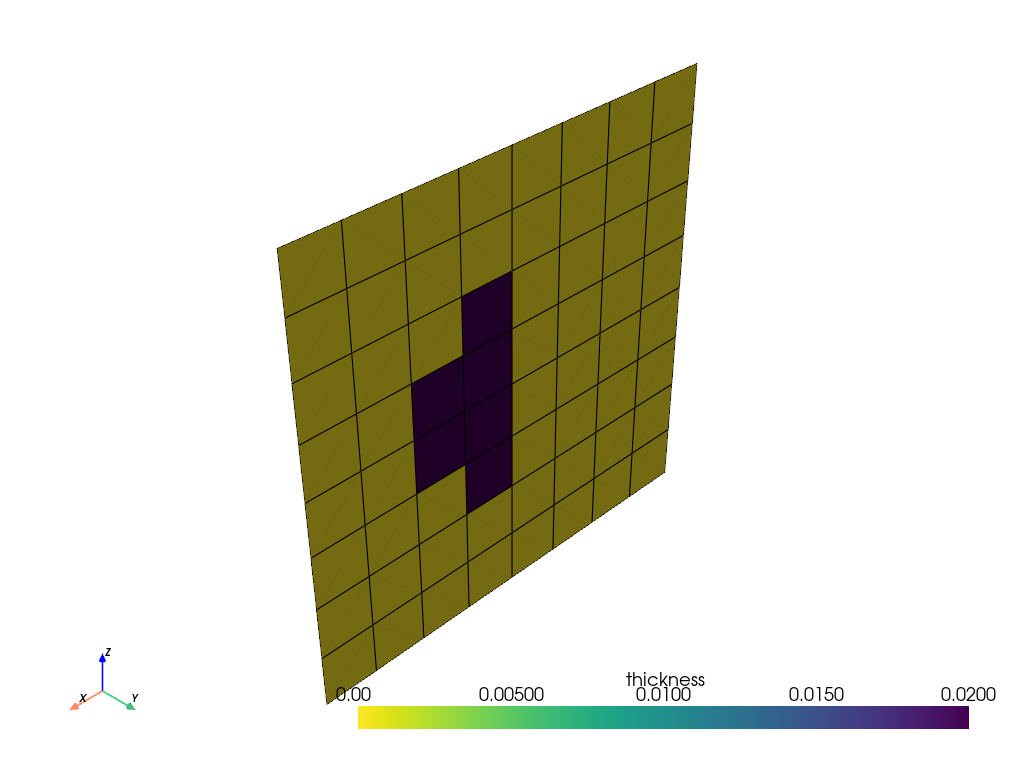
Modify the operation type of the Boolean selection rule so that the two rules are added.
linked_parallel_rule_boolean.operation_type = BooleanOperationType.INTERSECT
linked_cylindrical_rule_boolean.operation_type = BooleanOperationType.ADD
Plot the ply extent.
model.update()
assert model.elemental_data.thickness is not None
model.elemental_data.thickness.get_pyvista_mesh(mesh=model.mesh).plot(show_edges=True)
Total running time of the script: (0 minutes 7.716 seconds)