ModelingPly#
- class ansys.acp.core.ModelingPly(*, name='ModelingPly', ply_material=None, oriented_selection_sets=(), ply_angle=0.0, number_of_layers=1, active=True, global_ply_nr=0, selection_rules=(), draping_type='no_draping', draping_seed_point=(0.0, 0.0, 0.0), auto_draping_direction=True, draping_direction=(1.0, 0.0, 0.0), use_default_draping_mesh_size=True, draping_mesh_size=0.0, draping_thickness_correction=True, draping_angle_1_field=None, draping_angle_2_field=None, thickness_type='nominal', thickness_geometry=None, thickness_field=None, thickness_field_type='absolute_values', taper_edges=())#
Instantiate a Modeling Ply.
- Parameters:
name (str) – The name of the Modeling Ply
ply_material (Fabric | Stackup | SubLaminate | None) – The material (fabric, stackup or sub-laminate) of the ply.
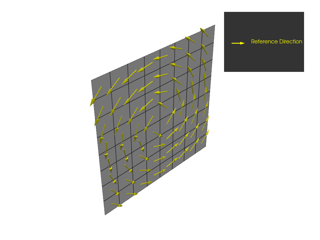
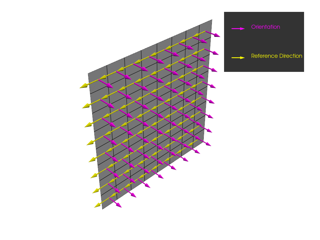
ply_angle (float) – Design angle between the reference direction and the ply fiber direction.
number_of_layers (int) – Number of times the plies are generated.
active (bool) – Inactive plies are ignored in ACP and the downstream analysis.
global_ply_nr (int) – Defines the global ply order.
selection_rules (Iterable[LinkedSelectionRule]) – Selection Rules which may limit the extent of the ply.
draping_type (DrapingType) – Chooses between different draping formulations.
draping_seed_point (tuple[float, float, float]) – Starting point of the draping algorithm.
auto_draping_direction (bool) –
- If
True, the fiber direction of the production ply at the draping seed point is used as draping direction.
- If
draping_direction (tuple[float, float, float]) – Set the primary draping direction for the draping algorithm. Only used if
auto_draping_directionisFalse.use_default_draping_mesh_size (bool) – Whether to use the average element size of the shell mesh for the draping.
draping_mesh_size (float) – Defines the mesh size for the draping algorithm. If set to
-1., the mesh size is automatically determined based on the average element size.draping_thickness_correction (bool) – Enables the thickness correction of draped plies based on the draping shear angle.
draping_angle_1_field (LookUpTable1DColumn | LookUpTable3DColumn | None) – Correction angle between the fiber and draped fiber directions, in degree.
draping_angle_2_field (LookUpTable1DColumn | LookUpTable3DColumn | None) – Correction angle between the transverse and draped transverse directions, in degree. Optional, uses the same values as
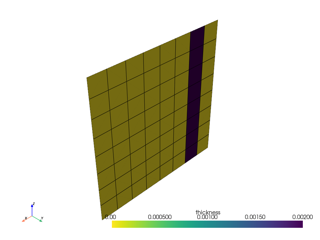
draping_angle_1_field(no shear) by default.thickness_type (ThicknessType) – Choose between
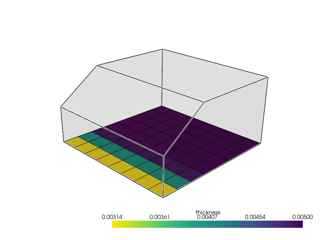
ThicknessType.FROM_GEOMETRYorThicknessType.FROM_TABLEto define a ply with variable thickness. The default value isThicknessType.NOMINAL, which means the ply thickness is constant and determined by the thickness of the ply material.thickness_geometry (VirtualGeometry | None) – Defines the geometry used to determine the ply thickness. Only applies if
thickness_typeisThicknessType.FROM_GEOMETRY.thickness_field (LookUpTable1DColumn | LookUpTable3DColumn | None) – Defines the look-up table column used to determine the ply thickness. Only applies if
thickness_typeisThicknessType.FROM_TABLE.thickness_field_type (ThicknessFieldType) – If
thickness_typeisThicknessType.FROM_TABLE, this parameter determines how the thickness values are interpreted. They can be either absolute values (ThicknessFieldType.ABSOLUTE_VALUES) or relative values (ThicknessFieldType.RELATIVE_SCALING_FACTOR).taper_edges (Iterable[TaperEdge]) – Defines the taper edges of the ply.
Added in ACP server version 24.2.
Methods
ModelingPly.add_selection_rule(selection_rule, *)Add a LinkedSelectionRule to the ModelingPly.
ModelingPly.add_taper_edge(edge_set, *, ...)Add a TaperEdge to the ModelingPly.
ModelingPly.clone(*[, unlink])Create a new unstored object with the same properties.
Delete the object.
ModelingPly.store(parent)Store the object on the server.
Attributes
Identifier of the object, used for example as key in maps.
Full mesh associated with the object.
The name of the object.
The parent of the object.
Shell mesh associated with the object.